
Typically, the impact analysis comes from the number of times others cite your work to demonstrate the validity and quality of one's work but also to analyze the number of published works. One's citations score should not be compared to another in a different discipline. Author impact refers to a number of metric styles. Examples for measuring the author impact include:
A number of tools may also be used to access these metrics. It should be noted not to rely on a single source of metrics but to gather various citation rankings.
What is it and how does it calculate?
The h-index, or Hirsch Index is used more than other metric styles. This was created by JE Hirsch's An index to quantify an individual's scientific research output in 2005. The h-Index identifies the number of papers h that have received h or more citations. Basically, if an author has an h-index of 8, then they have at least 8 publications with 8 or more citations. It aims to combine quality with quantity. The h-index has the potential to vary depending on the field.
Some free resources available to measure your h-index include:
*Important to note that not all searches in Google Scholar bring back scholarly works.
For more information on how to set up a Lens.org profile, check their website. Additionally, Lens.org can be helpful as it can be populated with data from ORCID, so it is recommended to have an up to date ORCID profile so Lens.org will more accurately reflect a scholar's research metrics.
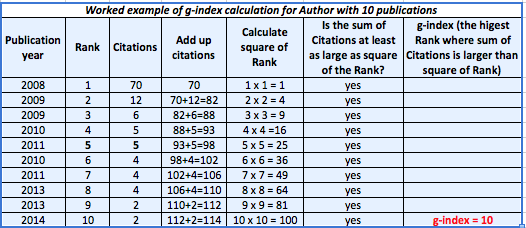
What is the g-index and how does it calculate?
The g-index was developed by Leo Egghe in his paper Theory and practice of the g-index, 2006. The g-index was designed to be an improvement to the h-index. Although the g-index is not as highly accepted as the h-index is in the academic community however, some do find the results to be effective. The g-index tends to weight highly cited articles more and it calculates the largest number n of highly cited articles for which the average number of citations is at least n. It intends to highlight the performance of an authors highly cited works. The caveat of this is that the g-index favors academics who publish more extensively of course. But the basic understand is that
Some free resources available to measure your g-index
Example
What is it and how does it calculate?
The i10-index was created by Google Scholar and it is calculated by the number of works with at least 10-citations by other authors. This metric is not overly complex as some of the others may be, but this is only used by Google Scholar.
*Important to note that not all searches in Google Scholar bring back scholarly works.
Example